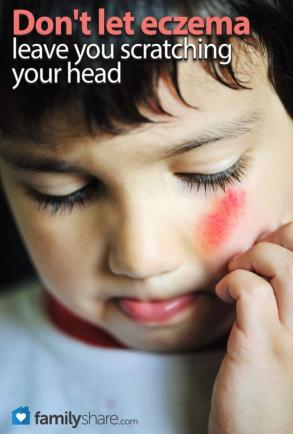
Eczema is a group of conditions that cause itchy and irritated red skin. Eczema can also cause fluid-filled bubbles. Atopic Dermatitis is the most common form and is known for its severity and intense itch. Doctors are not sure of the causes. It does appear to run in families.
Symptoms
Allergies seem to trigger the eczema, and it is thought to be a reaction of the immune system. It is not contagious, but one out of 10 people will be affected by it at some point in life. Eczema often appears in the bends of elbows and knees, on the face and on the neck. These patches may feel hot and itchy at first and then will become irritated after scratching. Symptoms vary from person to person, but are often seen as:
-
Dry, scaly or leathery skin
-
Sensitive skin
-
Intense itching
-
Red, inflamed skin or recurring rash
-
Skin that oozes or is crusty
-
Dark colored patches of skin
-
Areas of swelling
These symptoms do not have to be constant. Many people experience symptomatic periods and clear periods. Often eczema clears up by the age of 25.
Contributing factors
Some contributing factors to eczema are soaps and cleansers. It is best to use nondrying soaps and soaps that are not heavily perfumed. If you notice a flare-up after changing soap, then make sure it isn't the new soap causing the reaction. Use warm water when bathing because hot water dries the skin.
Sweating or overheating can contribute to Eczema. Keep areas clean from sweat, and keep as cool as possible. When using a towel, pat the skin dry. Rubbing the skin with a towel can irritate the skin. Choose smooth, soft fabrics to help protect the skin. Use gloves when cleaning to avoid contact with cleaning products. Stress can also trigger breakouts. Try to avoid scratching as this damages the skin and can cause the outbreak to become worse.
Treatments
Treatments can vary from simple to more complex.
-
Use ointments and creams, not lotions.
-
Avoid using creams or lotions with alcohol in them.
-
Moisturize immediately after bathing.
-
Apply a wet, cool compress to the affected area.
-
Use a humidifier.
-
Wear cool, smooth textured clothes.
-
Apply anti-itch or calamine lotion.
-
Sprinkle baking soda, uncooked oatmeal or colloidal oatmeal into a bath. Salt water baths are also thought to help.
-
Take an antihistamine to help stop itching.
-
Bleach baths help people who have problems with skin infections.
-
Phototherapy (exposing the skin to controlled amounts of sunlight) helps but has some risk involved due to exposure to the sun.
-
Antibiotics are used for people that develop skin infections.
-
Corticosteroids can help relieve itching and scaling but have some side effects from long-term use.
-
Immunomodulators work on the immune system to help regulate skin and are used when other treatments have failed.
Your doctor can help you decide which of the treatments are best for you. He may also send you to a Dermatologist, a doctor whose specialty is the skin. If after treatment it still does not clear up, then other allergies may be looked at as the cause.

