The Center for Disease Control and Prevention recently released a report stating that sexually transmitted diseases are at a record high in the United States.
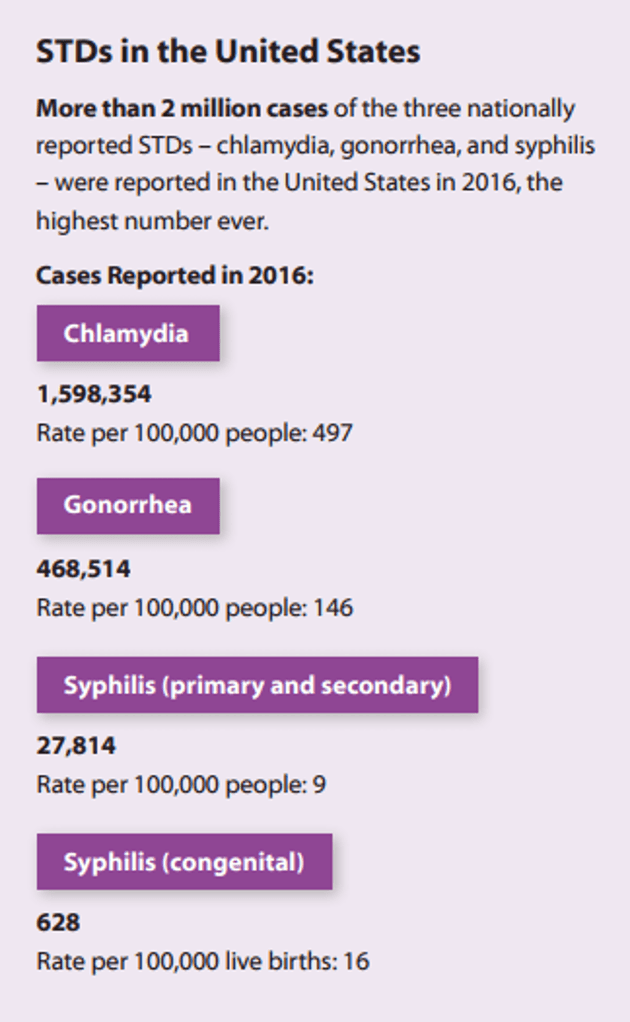
The study, which occurs annually, specifically looks at the STDs known as chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis. Here's a look at the numbers via this CDC Fact Sheet:
There's good news and bad news
The bad news is that STDs are on the rise and can cause severe problems. Young women diagnosed with chlamydia are especially at risk.
"Chlamydia is the most commonly reported STD, with approximately 1.6 million cases reported in 2016. Young women (ages 15-24) account for nearly half (46 percent) of reported cases and face the most severe consequences of an undiagnosed infection."
The report goes onto explain that untreated STDs "put women at increased risk for pelvic inflammatory disease which may result in chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and potentially a life-threatening ectopic pregnancy. It is estimated that undiagnosed STDs cause infertility in more than 20,000 women each year." What's more, is that some STDs like syphilis can pass from mother to baby, in the womb, causing severe health complications or death among newborns.
Sounds like quite a bit of bad news, doesn't it?
The good news is that all of these diseases are treatable with the proper antibiotics. It's imperative that people showing symptoms consult a physician for diagnosis, as soon as possible. Otherwise, if left untreated, "they put men, women, and infants at risk for severe, lifelong health outcomes like chronic pain, severe reproductive health complications, and HIV" according to the CDC.
What's the reason for the increase?
David Harvey, executive director of the National Coalition of STD Directors, recently told CNN that there are several factors that have contributed to such an epidemic. Things like reduced funding means fewer people are educated about preventing STDs. Additionally, "an on-going debate about sex education for young people, with cutbacks in that arena, particularly from this administration, and a rise in social media dating apps have all contributed to the rise."
What can be done?
The CDC suggests improved awareness at three levels in order to battle the rising trend:
-
Both the state and local health departments should put a focus on efforts to help people detect (and treat) STDs. The CDC suggests a higher emphasis treatment and detection in areas hit hardest by the STD epidemic.
-
Providers should help make STD screening a standard part of medical care. Pregnant women in particular should have easily accessible (and affordable) treatment and early detection methods. Prenatal care, care services and HIV prevention should also be made available.
-
And, last but not least, everyone should talk openly about STDs - awareness about being tested regularly, practicing mutual monogamy (or abstinence) and wearing protection when intimate can all help reduce the risk of STDs, if not prevent them entirely.